THE POLITICAL TRUST OF PEOPLE TOWARDS LOCAL POLITICIANS
Keywords:
Political trust, local politicianAbstract
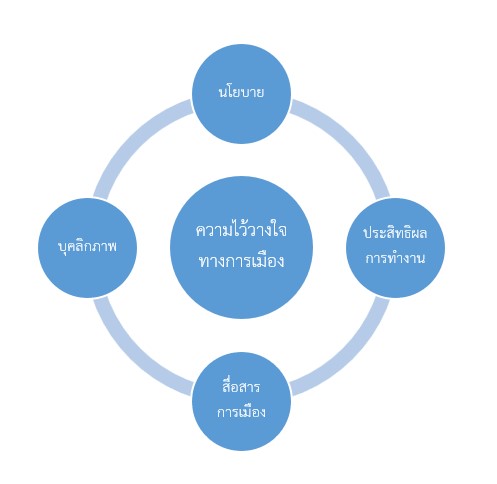
Trust is essential for public engagement with government agencies because citizens, as taxpayers and law-abiding individuals, expect transparency and accountability. Without trust, cooperation between the public and government deteriorates. Politicians, seen as public figures, are held to higher standards of responsibility, and their actions are closely monitored by the public, often through media channels. Citizens have expectations of the politicians they elect, and their trust is influenced by various factors. These include: 1. Policy-related aspects, such as 1.1 Local policies and 1.2 Public services; 2. Work efficiency; 3. Political communication; and 4. The personality of the politicians themselves.
References
Alongkorn Araksang. (2010). Development of Communication and Political Participation in Thai Society from 1957 to 2010. Bangkok: Thammasat University.
Bandura, A. (1977). Social Learning Theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Boies & Corbett, as cited in Knoll. (2007). The Relative Importance of Ability, Benevolence, and Integrity in Predicting Supervisor-Subordinate and Peer Trust (Unpublished master’s thesis). The University of Guelph, Guelph, Canada.
Citrin, J. (2007). “Political Alienation as a Social Indicator: Attitudes and Action.” Social Indicators Research, 4(1), 381-419.
Covey, S. R. (2004). The 8th Habit: From Effectiveness to Greatness. New York: Simon & Schuster.
Covey, S. R. (2006). Three Roles of Leadership in the New Paradigm. In F. Hesselbein & G. Dessler (Eds.), Personnel/Human Resource Management (5th ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Davis, J. H., Schoorman, F. D., Mayer, R. C., & Tan, H. H. (2000). “The Trusted General Manager and Business Unit Performance: Empirical Evidence of a Competitive Advantage.” Strategic Management Journal, 21, 563-576.
Dietz, Hartog, & Deanne. (2007). “A Robust Case for Strong Action to Reduce the Risks of Climate Change.” World Economics, 8(1), 121-168.
Gamson, W. A. (1968). Power and Discontent. Evanston, IL: The Dorsey Press.
Gerth, H., & Mills, C. W. (1964). Essays in Sociology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Hardin, R. (1999). Liberalism, Constitutionalism, and Democracy. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Healey, J. (2007). Radical Trust: How Today’s Great Leaders Convert People to Learning. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Kowit Puangngam. (2006). A New Dimension of Local Government: Vision of Decentralization and Local Administration. Faculty of Social Work. Bangkok: Thammasat University.
Kramer, R. M. (2006). Organizational Trust: A Reader. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Luhmann, N. (1979). Trust and Power: Two Works. Wiley.
McNair, B. (2003). An Introduction to Political Communication (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Routledge.
Office of the Civil Service Commission. (2007). Guidelines for Establishing Transparency Standards for Government Agencies.
Prin Boonchaloei. (2013). Organizational Culture, Learning Organization, and Organizational Effectiveness of the Judiciary: A Structural Equation Model (Doctoral dissertation in Social Development and Environmental Management). Faculty of Social Development and Environmental Management, National Institute of Development Administration.
Rosenberg. (1993). A Dictionary of Modern Politics (2nd ed.). London: Europa Publications Ltd.
Surapong Sothanasaethian. (1990). Communication and Society. Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Press.
Turton, A. (1987). Production, Power, and Participation in Rural Thailand: Experiences of Poor Farmers' Groups. Report for UNRISD.
Worapol Suphanuam. (2011). Problems and Obstacles in the Work of Police Officers in the Child and Women's Welfare Division (Master's thesis in Justice Administration). Faculty of Social Work, Thammasat University.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Modern Academic Social Science ISSN: 3056-9958 (Online)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.