Youth Political Participation in the Digital Era: Trends, Drivers, and Democratic Implications
คำสำคัญ:
Youth, Political Participation, Digital Era, Civic Engagement, Educationบทคัดย่อ
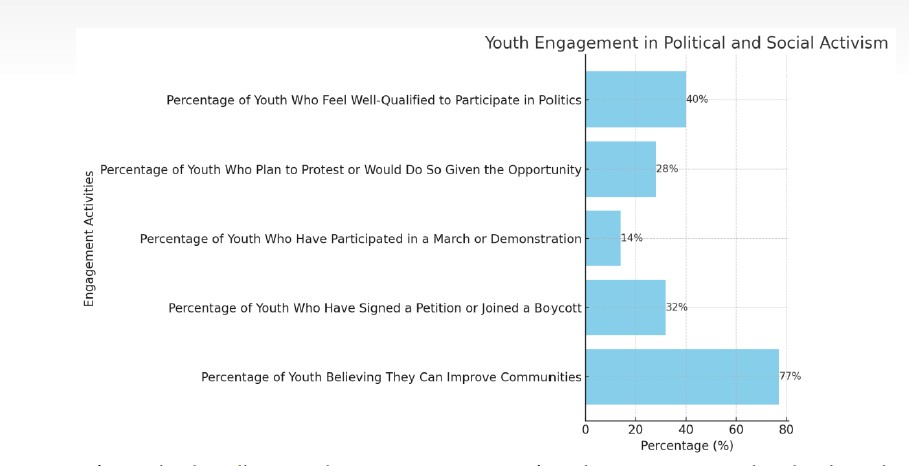
The study explores the evolving patterns of political participation among youth in the digital era, focusing on how technological advancements have redefined the ways in which young people engage with democratic processes. As digital platforms become increasingly integrated into daily life, they offer new spaces for civic expression, communication, and activism, particularly among the younger generation. This research aims to examine the current trends in youth political participation, identify key factors that drive such engagement, and assess the implications for democratic development. The study is grounded in a qualitative research methodology, employing document analysis and descriptive interpretation to explore youth behaviors, motivations, and challenges related to political participation. It highlights the importance of digital literacy, civic education, and critical thinking as foundational components in fostering informed and responsible participation. Findings reveal that while traditional forms of political engagement such as voting remain essential, there is a noticeable shift toward digital forms of participation, including online advocacy, social media activism, and participation in virtual forums and campaigns. The flexibility and immediacy of digital tools allow youth to express opinions, build networks, and organize movements more effectively than ever before. However, the study also notes that while digital engagement offers new opportunities, it also presents challenges such as misinformation, digital divides, and the potential for superficial involvement. To enhance meaningful youth political participation, it is crucial to implement strategies that combine digital empowerment with education that promotes ethical responsibility, critical inquiry, and community engagement. This study underscores the potential of youth as key actors in shaping political futures and emphasizes the need to support their active involvement through inclusive, informed, and digitally adaptive frameworks.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Abozaid, H. (2024). Impact of social media on politics. https://core.ac.uk/download/642713612.pdf
Achler, M., Krimmer, R., Kužel, R., Licht, S., et al. (2022). Elections in digital times: A guide for electoral practitioners. https://core.ac.uk/download/534010849.pdf
Adamu, A., Musa, F., Umar, M., Maswanku, M., Yahaya, M., et al. (2025). The strategies that can be employed to mitigate voter apathy and promote popular participation in Uganda. https://core.ac.uk/download/638687470.pdf
AP News. (2025). Untitled article. https://www.apnews.com/article/ff30e38698a41132cf90345fffabe579
Asante, J. (2020). African politics in the digital age: A study of political party-social media campaign strategies in Ghana. https://core.ac.uk/download/396458151.pdf
Aufderheide, P. (2003). In the battle for reality: Social documentaries in the U.S. https://core.ac.uk/download/71347989.pdf
Aulia, P. V., Danova, M. G., Furnamasari, Y. F., Sihombing, D. et al. (2024). Literature study: Dynamics of young generation political ethics in the digital era. https://core.ac.uk/download/617196248.pdf
Baboš, P., Białożyt, W., Blockmans, S., Bond, M., et al. (2020). Deliberative democracy in the EU: Countering populism with participation and debate. CEPS Paperback. https://core.ac.uk/download/288435926.pdf
Booth, R. B., Medina, A., Siegel-Stechler, K., & Kiesa, A. (2023). Youth are interested in political action, but lack support and opportunities. Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning and Engagement. https://circle.tufts.edu/latest-research/youth-are-interested-political-action-lack-support-and-opportunities
Booth, R. B., Medina, A., Siegel-Stechler, K., & Kiesa, A. (2023). Youth are interested in political action, but lack support and opportunities. Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning and Engagement. https://circle.tufts.edu/index.php/latest-research/youth-are-interested-political-action-lack-support-and-opportunities
Bowyer, B., Cohen, C., Middaugh, E., Rogowski, J., & Kahne, J. (2012). New media and youth political action. https://core.ac.uk/download/71361981.pdf
Canty, A. (2023). New poll: Majority of youth ready to make an impact in 2024 election. Common Cause. https://www.commoncause.org/es/prensa/new-poll-majority-of-youth-ready-to-make-an-impact-in-2024-election/
Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning and Engagement. (2025). Broadening youth voting. https://circle.tufts.edu/research-areas/broadening-youth-voting
de Ridder, S., Hartley, J. M., Kleut, J., Pavlíčková, T., et al. (2017). Small acts of audience engagement interrupting content flows. https://core.ac.uk/download/388956215.pdf
Della Volpe, J. (2024). 47th Harvard youth poll results: Five findings relevant to voting. Harvard Kennedy School Institute of Politics. https://www.usvotefoundation.org/47th-harvard-youth-poll-results-five-findings-relevant-voting
Espada, M. (2020). ‘We’ve seen a youthquake.’ How youth of color backed Joe Biden in battleground states. Time. https://time.com/5910291/weve-seen-a-youthquake-how-youth-of-color-backed-joe-biden-in-battleground-states/
Espada, M. (2020). ‘We’ve seen a youthquake.’ How youth of color backed Joe Biden in battleground states. Time. https://time.com/5910291/weve-seen-a-youthquake-how-youth-of-color-backed-joe-biden-in-battleground-states/
Firestone, C., Lasica, J. D., & Kelly, P. (2007). The mobile generation: Global transformations at the cellular level. https://core.ac.uk/download/71339786.pdf
Hobbs, R. (2010). Digital and media literacy: A plan of action. https://core.ac.uk/download/71347458.pdf
Institute of Politics at Harvard Kennedy School. (2023). Harvard youth poll: 46th edition, fall 2023. Harvard Kennedy School. https://iop.harvard.edu/youth-poll/46th-edition-fall-2023
Johnson, F., & Menichelli, K. (2007). What’s going on in community media. https://core.ac.uk/download/71339790.pdf
Koc-Michalska, K., Lilleker, D., & Surowiec, P. (2012). Broadcasting to the masses or building communities: Polish political parties online communication during the 2011 election. https://core.ac.uk/download/19963970.pdf
Leach, M. (2016). States, markets and society – Looking back to look forward. https://core.ac.uk/download/286047752.pdf
Levine, P. (2008). A public voice for youth: The audience problem in digital media and civic education. https://core.ac.uk/download/71339814.pdf
Mo, C. H., Holbein, J. B., & Elder, E. M. (2022). Civilian national service programs can powerfully increase youth voter turnout. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(29), e2122996119. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9304004/
Obisesan, O. F. (2022). The ‘#tag Generation’: Social media and youth participation in the 2019 general election in Nigeria. https://core.ac.uk/download/544237540.pdf
Olorunfemi, F. (2022). The political economy of state fragility and the extent to which it fuels international migration amongst Nigerians. https://core.ac.uk/download/554011053.pdf
Robinson, S. (2023). Michigan had country’s highest youth turnout in 2022 midterms. Axios. https://www.axios.com/local/detroit/2023/04/20/michigan-highest-youth-turnout-2022-midterms
Singh, S. (2024). In what ways does the rise of China’s emerging cognitive warfare capabilities pose a threat to South-East Asia? https://core.ac.uk/download/618458559.pdf
Soukup, P. A. (2015). Smartphones. https://core.ac.uk/download/215444184.pdf
UNESCO – United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. (2025). Keystones to foster inclusive knowledge societies: Access to information and knowledge, freedom of expression, privacy, and ethics on a global internet. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/30671829.pdf
United Way of the National Capital Area. (2024). The Gen Z activism survey. https://unitedwaynca.org/blog/gen-z-activism-survey/
Vote.org. (2023). Vote.org reports big spikes in voter registrations in key states across the country, among younger voters. https://www.vote.org/blog/2023electionstats/
Wang, Q., Lu, M., & Li, Q. (2020). Interactive, multiscale urban-traffic pattern exploration leveraging massive GPS trajectories. Sensors, 20(4), 1084. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7070530/
Wikipedia. (2020). Social media in the 2020 United States presidential election. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_media_in_the_2020_United_States_presidential_election
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารวิชาการสังคมศาสตร์สมัยใหม่ (Online)

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.